
Gamete: Now after meiosis, there are four daughter cells which if male, are four sperm cells and if female, are one egg cell and three other cells that form around the egg cell. Telophase II: In this stage the cells start dividing and the nuclear membrane reforms around the chromatids. Anaphase II: This is the stage where the chromatids seperate and start moving towards opposite sides of the cells. 
Metaphase II: In this stage the sister chromatids line up at the center and the spindle fibres attach and start pulling on them.
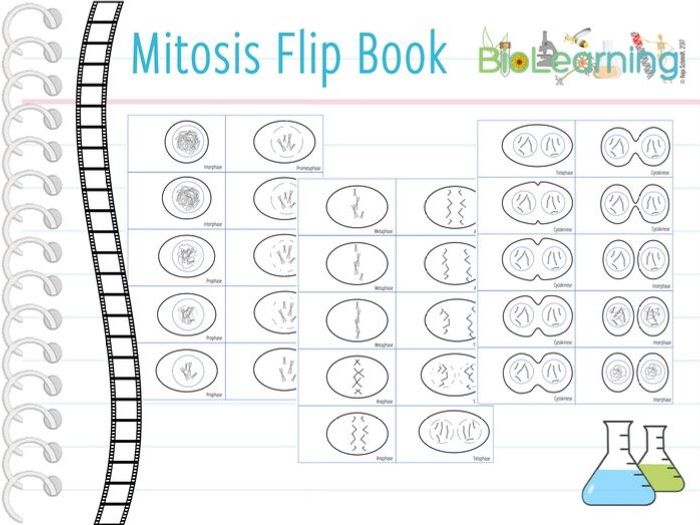 Prophase II: In this stage the centrosomes start moving to opposite sides of each cell. Telophase 1: In this stage the nuclear membrane forms again around the chromatid, the two daughter cells forming are haploid. The condensed chromatin expands and the nuclear envelope reappears. Mitosis Simulation Activity: Maria Maureen Sado, Aimee George, Julianne Maniago, Kelly Novak. Scribd is the worlds largest social reading and publishing site. Actually, mitosis is a kind of karyokinesis, or. The goal of mitosis is to distribute pre-combined genetic material equally. Mitosis does not change the cells’ genotype.
Prophase II: In this stage the centrosomes start moving to opposite sides of each cell. Telophase 1: In this stage the nuclear membrane forms again around the chromatid, the two daughter cells forming are haploid. The condensed chromatin expands and the nuclear envelope reappears. Mitosis Simulation Activity: Maria Maureen Sado, Aimee George, Julianne Maniago, Kelly Novak. Scribd is the worlds largest social reading and publishing site. Actually, mitosis is a kind of karyokinesis, or. The goal of mitosis is to distribute pre-combined genetic material equally. Mitosis does not change the cells’ genotype. 
Anaphase 1: In this stage the chromatids start moving to opposite ends of the cell as the spindle fibres pull. Mitosis-Simulation-Activitystudent - Read online for free. Mitosis is a process of equal cell division, where each of the new cells receives the same number of chromosomes as the original cell.Metaphase 1: In this stage the chromatids line up in the center of the cell, and the spindle fibres attach to the chromatids.Prophase 1: In this stage the chromatids connect and cross over, this is when the chromatids trade sections.Meiosis Slideshow The stages of Meiosis.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
